|
PC机与单片机的通讯
大多数的电脑设备都具有RS-232C接口,尽管它的性能指标并非很好。在广泛的市场支持下依然常胜不衰。就使用而言,RS-232也确实有其优势:仅需3根线便可在两个数字设备之间全双工的传送数据。不过,RS-232C的控制要比使用并行通讯的打印机接口更难于控制。RS-232C使用了远较并行口更多的寄存器。这些寄存器用来实现串行数据的传送及RS-232C设备之间的握手与流量控制。本文将分别描述PC机及单片机MCS-51的串行通讯的原理及具体的软件设计。
(1)RS-232C介绍与PC硬件:
RS-232C使用-3到-25V表示数字“1”,使用3V到25V表示数字“0”,RS-232C在空闲时处于逻辑“1”状态,在开始传送时,首先产生一起始位,起始位为一个宽度的逻辑“0”,紧随其后为所要传送的数据,所要传送的数据有最低位开始依此送出,并以一个结束位标志该字节传送结束,结束位为一个宽度的逻辑“1”状态。
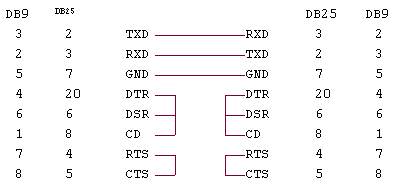
PC机一般使用8250或16550作为串行通讯的控制器,使用9针或25针的接插件将串行口的信号送出。该插座的信号定义如下:
| DB-25 |
DB-9 |
信号名称 |
方向 |
含 义 |
| 2 |
3 |
TXD |
输出 |
数据发送端 |
| 3 |
2 |
RXD |
输入 |
数据接收端 |
| 4 |
7 |
RTS |
输出 |
请求发送(计算机要求发送数据) |
| 5 |
8 |
CTS |
输入 |
清除发送(MODEM准备接收数据) |
| 6 |
6 |
DSR |
输入 |
数据设备准备就绪 |
| 7 |
5 |
SG |
- |
信号地 |
| 8 |
1 |
DCD |
输入 |
数据载波检测 |
| 20 |
4 |
DTR |
输出 |
数据终端准备就绪(计算机) |
| 22 |
9 |
RI |
输入 |
响铃指示 |
以上信号在通讯过程之中可能会被全部或部分使用,最简单的通讯仅需TXD及RXD及SG即可完成,其他的握手信号可以做适当处理或直接悬空,至于是否可以悬空这视乎你的通讯软件。比如说,如果使用DOS所提供的BIOS通讯驱动程序,那么,这些握手信号则需要做如下处理,因为BIOS的通讯驱动使用了这些信号。如果使用自己编写的串行驱动程序则可以完全不使用这些握手信号(详见下面有关章节)。
PC机一般使用8250或16550的作为串行通讯控制器,8250及16550的管脚排列如下:

8250(16550)的寄存器如下表所示:
| 基地址 |
读/写 |
寄存器缩写 |
注 释 |
| 0 |
Write |
- |
发送保持寄存器(DLAB=0) |
| 0 |
Read |
- |
接收数据寄存器(DLAB=0) |
| 0 |
Read/Write |
- |
波特率低八位(DLAB=1) |
| 1 |
Read/Write |
IER |
中断允许寄存器 |
| 1 |
Read/Write |
- |
波特率高八位(DLAB=1) |
| 2 |
Read |
IIR |
中断标识寄存器 |
| 2 |
Write |
FCR |
FIFO控制寄存器 |
| 3 |
Read/Write |
LCR |
线路控制寄存器 |
| 4 |
Read/Write |
MCR |
MODEM控制寄存器 |
| 5 |
Read |
LSR |
线路状态寄存器 |
| 6 |
Read |
MSR |
MODEM状态寄存器 |
| 7 |
Read/Write |
- |
Scratch Register |
PC机支持1-4个串行口,即COM1-COM4,其基地址在BIOS数据区0000:0400-0000:0406中描述,对应地址分别为3F8/2F8/3E8/2E8,COM1及COM3使用PC机中断4,COM2及COM4使用中断3。
在上表中,8250共有12个寄存器,使用了8个地址,其中部分寄存器共用一个地址,由DLAB=0/1来区分,在DLAB=1用于设定通讯所需的波特率。常用的波特率参数见下表:
| 速率(BPS) |
波特率高八位 |
波特率低八位 |
| 50 |
09h |
00h |
| 300 |
01h |
80h |
| 600 |
00h |
C0h |
| 2400 |
00h |
30h |
| 4800 |
00h |
18h |
| 9600 |
00h |
0Ch |
| 19200 |
00h |
06h |
| 38400 |
00h |
03h |
| 57600 |
00h |
02h |
| 115200 |
00h |
01h |
以下几个表格为8250的寄存器的功能描述:
中断允许寄存器(IER):
| 位 |
注 释 |
| 7 |
未使用 |
| 6 |
未使用 |
| 5 |
进入低功耗模式(16750) |
| 4 |
进入睡眠模式(16750) |
| 3 |
允许MODEM状态中断 |
| 2 |
允许接收线路状态中断 |
| 1 |
允许发送保持器空中断 |
| 0 |
允许接收数据就绪中断 |
Bit0置1将允许接收到数据时产生中断,Bit1置1时允许发送保持寄存器空时产生中断,Bit2置1将在LSR变化时产生中断,相应的Bit3置位将在MSR变化时产生中断。
中断识别寄存器(IIR):
| 位 |
注 释 |
| Bit6:7=00 |
无FIFO |
| Bit6:7=01 |
允许FIFO,但不可用 |
| Bit6:7=11 |
允许FIFO |
| Bit5 |
允许64字节FIFO(16750) |
| Bit4 |
未使用 |
| Bit3 |
16550超时中断 |
| Bit2:1=00 |
MODEM状态中断(CTS/RI/DTR/DCD) |
| Bit2:1=01 |
发送保持寄存器空中断 |
| Bit2:1=10 |
接收数据就绪中断 |
| Bit2:1=11 |
接收线路状态中断 |
| Bit0=0 |
有中断产生 |
| Bit0=1 |
无中断产生 |
IIR为只读寄存器,Bit6:7用来指示FIFO的状态,均为0时则无FIFO,此时为8250或16450芯片,为01时有FIFO但不可以使用,为11时FIFO有效并可以正常工作。Bit3用来指示超时中断(16550/16750)。
Bit0用来指示是否有中断发生,Bit1:2标识具体的中断类型,这些中断具有不同的优先级别,其中LSR中断级别最高,其次是数据就绪中断,然后是发送寄存器空中断,而MSR中断级别最低。
FIFO控制寄存器(FCR):
| 位 |
注 释 |
| Bit7:6=00 |
1Byte产生中断 |
| Bit7:6=01 |
4Byte产生中断 |
| Bit7:6=10 |
8Byte产生中断 |
| Bit7:6=11 |
14Byte产生中断 |
| Bit5 |
允许64字节FIFO |
| Bit4 |
未使用 |
| Bit3 |
DMA模式选择 |
| Bit2 |
清除发送FIFO |
| Bit1 |
清除接收FIFO |
| Bit0 |
允许FIFO |
FCR可写但不可以读,该寄存器用来控制16550或16750的FIFO寄存器。Bit0置1将允许发送/接收的FIFO工作,Bit1和Bit2置1分别用来清除接收及发送FIFO。清除接收及发送FIFO并不影响移位寄存器。Bit1:2可自行复位,因此无需使用软件对其清零。Bit6:7用来设定产生中断的级别,发送/接收中断将在发送/接收到对应字节数时产生。
线路控制寄存器(LCR):
| 位 |
注 释 |
| Bit7=1 |
允许访问波特率因子寄存器 |
| Bit7=0 |
允许访问接收/发送及中断允许寄存器 |
| Bit6 |
设置间断,0-禁止,1-设置 |
| Bit5:3=XX0 |
无校验 |
| Bit5:3=001 |
奇校验 |
| Bit5:3=011 |
偶校验 |
| Bit5:3=101 |
奇偶保持为1 |
| Bit5:3=111 |
奇偶保持为0 |
| Bit2=0 |
1位停止位 |
| Bit2=1 |
2位停止位(数据位6-8位),1.5位停止位(5位数据位) |
| Bit1:0=00 |
5位数据位 |
| Bit1:0=01 |
6位数据位 |
| Bit1:0=10 |
7位数据位 |
| Bit1:0=11 |
8位数据位 |
LCR用来设定通讯所需的一些基本参数。Bit7为1指定波特率因子寄存器有效,为0则指定发送/接收及IER有效。Bit6置1会将发送端置为0,这将会使接收端产生一个“间断”。Bit3-5用来设定是否使用奇偶校验以及奇偶校验的类型,Bit3=1时使用校验,Bit4为0则为奇校验,1为偶校验,而Bit5则强制校验为1或0,并由Bit4决定具体为0或1。Bit2用来设定停止位的长度,0表示1位停止位,为1则根据数据长度的不同使用1.5-2位停止位。Bit0:1用来设定数据长度。
MODEM控制寄存器(MCR):
| 位 |
注 释 |
| Bit7 |
未使用 |
| Bit6 |
未使用 |
| Bit5 |
自动流量控制(仅16750) |
| Bit4 |
环路测试 |
| Bit3 |
辅助输出2 |
| Bit2 |
辅助输出1 |
| Bit1 |
设置RTS |
| Bit0 |
设置DSR |
MCR寄存器可读可写,Bit4=1进入环路测试模式。Bit3-0用来控制对应的管脚。
线路状态寄存器(LSR):
| 位 |
注 释 |
| Bit7 |
FIFO中接收数据错误 |
| Bit6 |
发送移位寄存器空 |
| Bit5 |
发送保持寄存器空 |
| Bit4 |
间断 |
| Bit3 |
帧格式错 |
| Bit2 |
奇偶错 |
| Bit1 |
超越错 |
| Bit0 |
接收数据就绪 |
LSR为只读寄存器,当发生错误时Bit7为1,Bit6为1时标示发送保持及发送移位寄存器均空,Bit5为1时标示仅发送保持寄存器空,此时,可以由软件发送下一数据。当线路状态为0时Bit4置位为1,帧格式错时Bit3置位为1,奇偶错和超越错分别将Bit2及Bit1置位为1。Bit0置位为1表示接收数据就绪。
MODEM状态寄存器(MSR):
| 位 |
注 释 |
| Bit7 |
载波检测 |
| Bit6 |
响铃指示 |
| Bit5 |
DSR准备就绪 |
| Bit4 |
CTS有效 |
| Bit3 |
DCD已改变 |
| Bit2 |
RI已改变 |
| Bit1 |
DSR已改变 |
| Bit0 |
CTS已改变 |
MSR寄存器的高4位分别对应MODEM的状态线,低4位表示MODEM的状态线是否发生了变化。
以上我们详细介绍了PC机的串行通讯硬件环境,以下将分别给出使用查询及中断驱动的方法编写的串行口驱动程序。这些程序仅使用RXD/TXD,无需硬件握手信号。
(2)使用查询方法的串行通讯程序设计: 返回页首
polling.c 下载polling.c
#include <dos.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define PortBase 0x2F8
void com_putch(unsigned char);
int com_chkch(void);
main()
{
int c;
unsigned char ch;
outportb(PortBase +1,0);/*Turn off interrupts -Port1*/
/*Set COM1:9600,8,N,1*/
outportb(PortBase +3,0x80);
outportb(PortBase +0,0x0C);
outportb(PortBase +1,0x00);
outportb(PortBase +3,0x03);
clrscr();
while(1){
c =com_chkch();
if(c!=-1){
c &=0xff;putch(c);
if(c=='\n')putch('\r');
}
if(kbhit()){
ch =getch();com_putch(ch);
}
}
}
void com_putch(unsigned char ch){
unsigned char status;
while(1){
status =inportb(PortBase+5);
if(status&0x01)inportb(PortBase+0);else break;
}
outportb(PortBase,ch);
}
int com_chkch(void){
unsigned char status;
status =inportb(PortBase+5);
status &=0x01;
if(status)return((int)inportb(PortBase+0));else return(-1);
}
使用查询方式的通讯程序适合9600bps以下的应用。
(3)使用中断的串行通讯程序设计: 返回页首
该程序由两部分组成,serial.c及sercom.c,sercom.c为通讯的底层驱动,使用中断的串行通讯程序可以工作到115.2Kbps.
serial.c 下载serial.c
#include <dos.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <bios.h>
#include "sercom.c"
COM*c;
main()
{
unsigned char ch;
c =ser_init(PORT_B,BAUD_9600,_COM_CHR8,_COM_NOPARITY,4096,4096);
while(1){
if(serhit(c)){
ch =getser(c);
putchar(ch);
}
if(kbhit()){
ch =getch();
putser(ch,c);
}
}
}
llio.c 下载llio.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dos.h>
#include <bios.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define CR0x0d
#define TRUE0xff
#define FALSE0
#define PORT_A 0/*COM1*/
#define PORT_B 1/*COM2*/
#define BAUD_9600 _COM_9600
#define BAUD_4800 _COM_4800
#define BAUD_2400 _COM_2400
#define BAUD_1200 _COM_1200
#define BAUD_600 _COM_600
#define BAUD_300 _COM_300
#define BAUD_110 _COM_110
typedef struct {
char ready; /*TRUEwhen ready */
unsigned com_base; /*8250Base Address */
char irq_mask; /*IRQ Enable Mask */
char irq_eoi; /*EOIreply for this port */
char int_number; /*Interrupt #used */
void (_interrupt _far *old)(void ); /*Old Interrupt */
/*Buffers for I/O*/
char *in_buf; /*Input buffer */
int in_tail; /*Input buffer TAILptr */
int in_head; /*Input buffer HEADptr */
int in_size; /*Input buffer size */
int in_crcnt; /*Input <CR>count */
char in_mt; /*Input buffer FLAG*/
char *out_buf; /*Output buffer */
int out_tail; /*Output buffer TAILptr */
int out_head; /*Output buffer HEADptr */
int out_size; /*Output buffer size */
char out_full; /*Output buffer FLAG*/
char out_mt; /*Output buffer MT*/
}COM;
COM *ser_init(int port,int baud,int bit,int parity,int isize,int osize );
void ser_close(COM*c );
int getsers(COM*c,int len,char *str );
int putsers(char *str,COM*c );
char serline(COM*c );
int getser(COM*c );
char serhit(COM*c);
char putser(char outch,COM*c);
void cntl_rts(int flag,COM*c);
void cntl_dtr(int flag,COM*c);
void clean_ser(COM*c );
#define COM1_BASE 0x03F8
#define COM1_IRQ_MASK 0xEF /*11101111BIRQ4For COM1*/
#define COM1_IRQ_EOI 0x64 /*IRQ4Spec EOI*/
#define COM1_INT_NUM 0x0C /*Int #for IRQ4*/
#define COM2_BASE 0x02F8
#define COM2_IRQ_MASK 0xF7 /*11110111BIRQ3For COM2*/
#define COM2_IRQ_EOI 0x63 /*IRQ3Spec EOI*/
#define COM2_INT_NUM 0x0B /*Int #for IRQ3*/
/*8250ACEregister defs */
#define THR 0 /*Offset to Xmit hld reg (write)*/
#define RBR 0 /*Receiver holding buffer (read)*/
#define IER 1 /*Interrupt enable register */
#define IIR 2 /*Interrupt identification reg */
#define LCR 3 /*Line control register */
#define MCR 4 /*Modem control register */
#define LSR 5 /*Line status register */
#define MSR 6 /*Modem status register */
#define SREG(x) ((unsigned)((unsigned)x +c->com_base))
/*8259Int controller registers */
#define INTC_MASK 0x21 /*Interrupt controller MASKreg */
#define INTC_EOI 0x20 /*Interrupt controller EOIreg */
#define MAX_PORTS 2 /*#I/Oports (DOSlimit)*/
static int count =0;
static COM com_list[MAX_PORTS]; /*I/Odata structure */
static COM *com1; /*Pointers for
interrupt actions */
static COM *com2;
static COM *com_xfer; /*Transfer interrupt data structure */
COM *ser_init0(int port,char *ibuf,int isize,char *obuf,int osize);
void ser_close0(COM*c );
void (_interrupt _far int_ser1)(void ); /*Int rtn for serial I/O COM1*/
void (_interrupt _far int_ser2)(void ); /*Int rtn for serial I/O COM2*/
void (_interrupt _far int_ser_sup)(void );/*Support int actions */
COM *ser_init(int port,int baud,int bit,int parity,int isize,int osize )
{
unsigned status;
char ch;
COM*c;
char *in_buf,*out_buf;
status =_bios_serialcom(_COM_INIT,port,(bit |parity |_COM_STOP2|baud ));
in_buf =malloc(isize );
if(in_buf ==NULL)return(NULL);
out_buf =malloc(osize );
if(out_buf ==NULL)return(NULL);
c =ser_init0(port,in_buf,isize,out_buf,osize );
clean_ser(c);
return(c );
}
void ser_close(COM*c)
{
int i;
if(!c->ready )return;
ser_close0(c);
free(c->in_buf );
free(c->out_buf );
}
char serline(COM*c )
{
if(!c->ready )return(FALSE);
if(c->in_crcnt >0)return(TRUE);
else return(FALSE);
}
int getsers(COM*c,int len,char *str )
{
char ch;
int i;
i =0;
while(i<len ){
while(!serhit(c)){
if(kbhit())return(-1);
}
ch =0x7f &getser(c);
switch(ch ){
case 0x0d:str[i++]='\0';
return(i );
case 0x00:
case 0x0a:break;
default:str[i++]=ch;
break;
}
}
str[i]='\0';
return(len );
}
int putsers(char *str,COM*c )
{
int n,i,j;
n =strlen(str );
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
while(!putser(str[i],c ));
}
return(n );
}
char putser(char outch,COM*c )
{
char val;
if(!c->ready )return(FALSE);
while(!c->out_mt &&(c->out_head ==c->out_tail));
if(!c->out_full ){
c->out_buf[c->out_head++]=outch;
if(c->out_head ==c->out_size )
c->out_head =0; /*Reset buffer circularly */
}
if(c->out_head ==c->out_tail ){
c->out_full =TRUE;
return(FALSE);
}else c->out_full =FALSE;
val =inp(SREG(LCR)); /*Reset DLABfor IERaccess */
val &=0x7F; /*Clear IERaccess bit */
outp(SREG(LCR),val);
val =inp(SREG(IER));
if(!(val &0x02)) /*Interrupt ON?*/
{
c->out_mt =FALSE; /*Not MTnow */
_disable(); /*Interrupts OFF NOW*/
outp(SREG(IER),0x03); /*RX&TXinterrupts ON*/
_enable(); /*Interrupts ONagain */
}
return(TRUE);
}
char serhit(COM*c )
{
if(!c->ready )return(FALSE);
if(!c->in_mt )return(TRUE);
else return(FALSE);
}
int getser(COM*c )
{
int ch;
if(!c->ready )return(FALSE);
if(!serhit(c))return(0);
_disable();
ch =0xff &c->in_buf[c->in_tail++];
if(c->in_tail ==c->in_size )c->in_tail =0;
if(c->in_tail ==c->in_head )c->in_mt =TRUE;
if(ch ==CR) /*Keep track of CR's */
c->in_crcnt--;
_enable();
return(ch );
}
void clean_ser(COM*c )
{
_disable();
c->in_head =0;
c->in_tail =0;
c->in_mt =TRUE;
c->in_crcnt =0;
_enable();
}
void cntl_dtr(int flag,COM*c )
{
char val;
if(!c->ready )return;
val =inp(SREG(MCR));
if(flag )val |=1;
else val &=~1;
outp(SREG(MCR),val);
}
void cntl_rts(int flag,COM*c )
{
char val;
if(!c->ready )return;
val =inp(SREG(MCR));
if(flag )val |=2;
else val &=~2;
outp(SREG(MCR),val);
}
COM *ser_init0(int port,char *ibuf,int isize,char *obuf,int osize)
{
int i;
char val;
COM*c;
while(port >=MAX_PORTS) /*Get port #in range */
port--;
for(i=0;i<MAX_PORTS;i++)/*Select data structure */
{
if(!com_list[i].ready ){
c =&(com_list[i]);
break;
}
}
if(i ==MAX_PORTS)/*Not found */
return(NULL);
c->in_buf =ibuf;
c->in_size =isize;
c->in_mt =TRUE;
c->in_head =0;
c->in_tail =0;
c->in_crcnt =0;
c->out_buf =obuf;
c->out_size =osize;
c->out_full =FALSE;
c->out_mt =TRUE;
c->out_head =0;
c->out_tail =0;
switch(port ){
case 0: /*Here set up for COM1*/
c->ready =TRUE;
c->com_base =COM1_BASE;
c->irq_mask =COM1_IRQ_MASK;
c->irq_eoi =COM1_IRQ_EOI;
c->int_number =COM1_INT_NUM;
_disable();
com1=c;
c->old =_dos_getvect(c->int_number );
_dos_setvect(c->int_number,int_ser1);
break;
case 1: /*Here set up for COM1*/
c->ready =TRUE;
c->com_base =COM2_BASE;
c->irq_mask =COM2_IRQ_MASK;
c->irq_eoi =COM2_IRQ_EOI;
c->int_number =COM2_INT_NUM;
_disable();
com2=c;
c->old =_dos_getvect(c->int_number );
_dos_setvect(c->int_number,int_ser2);
break;
default:return(NULL); /*Bad port SKIP*/
}
val =inp(INTC_MASK);
val &=c->irq_mask;
outp(INTC_MASK,val );
val =inp(SREG(LSR)); /*Read and discard STATUS*/
val =inp(SREG(RBR)); /*Read and discard DATA*/
val =inp(SREG(LCR)); /*Rst DLABfor IERaccess */
val &=0x7F; /*01111111B*/
outp(SREG(LCR),val );
outp(SREG(IER),1); /*Enable Data READY INT*/
outp(SREG(MCR),0xB); /*Enable OUT2,RTS&DTR*/
_enable();
return(c );
}
void ser_close0(COM*c )
{
char val;
if(!c->ready )return;
_disable();
val =inp(INTC_MASK);
val |=~c->irq_mask;
outp(INTC_MASK,val);
val =inp(SREG(LCR)); /*Reset DLABfor IERaccess */
val &=0x7F; /*Clear IERaccess bit */
outp(SREG(LCR),val);
val =inp(SREG(RBR));
val =inp(SREG(LSR));
val =inp(SREG(IIR));
val =inp(SREG(IER));
outp(SREG(IER),0); /*Disable 8250Interrupts */
outp(SREG(MCR),0); /*Disable RTS,DTRand OUT2*/
outp(SREG(MCR),0); /*Disable OUT2*/
_dos_setvect(c->int_number,c->old );
_enable();
c->ready =FALSE;
}
void _interrupt _far int_ser1(void )
{
com_xfer =com1;
_chain_intr(int_ser_sup );
}
void _interrupt _far int_ser2(void )
{
com_xfer =com2;
_chain_intr(int_ser_sup );
}
void _interrupt _far int_ser_sup(void )
{
char val;
char ch;
int ptr;
COM*c;
c =com_xfer;
while(TRUE){
val =inp(SREG(LSR));/*Read and discard STATUS*/
val =inp(SREG(IIR));/*Get interrupt status register */
if(val &0x04)/*Receive Interrupt */
{
ptr =c->in_head;
ch =inp(SREG(RBR));
if(c->in_mt ||ptr !=c->in_tail ){
c->in_buf[ptr++]=ch;
if(ptr ==c->in_size )ptr =0;
c->in_head =ptr;
c->in_mt =FALSE;
if(ch ==CR) /*Count lines */
c->in_crcnt++;
}
}else {
if(val &0x02)/*Transmit Interrupt */
{
if((!c->out_full)&&(c->out_head ==c->out_tail)){
c->out_mt =TRUE;
val =inp(SREG(LCR));
val &=0x7F;
outp(SREG(LCR),val);
outp(SREG(IER),0x01);
/*RXinterrupts ON*/
}else {
outp(SREG(THR),
c->out_buf[c->out_tail++]);
if(c->out_tail ==c->out_size )c->out_tail =0;
}
}else return; /*No Interrupt */
}
outp(INTC_EOI,c->irq_eoi);
}
}
(4)MCS-51串行通讯: 下载serint.c 下载serint.h
MCS-51的串行口使用起来非常简单,因为MCS-51单片机的串行口没有与MODEM控制相关的信号。这使得51的通讯口非常易于使用。使用查询方式时,仅需初始化有关的寄存器即可。演示程序如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <reg51.h>
void putch(unsigned char);
unsigned char getch(void);
main()
{
unsigned char ch;
SCON=0x50;
TMOD|=0x20;
TH1=0xfd;
TL1=0xfd;
TR1=1;
TI=1;
RI=0;
while(1){
ch =getch();putch(ch);
}
}
void putch(unsigned char ch){
SBUF=ch;
TI=0;
while(!TI);
}
unsigned char getch(void){
while(!RI);
RI=0;
return(SBUF);
}
使用中断驱动的程序比较复杂,下面为完整的MCS-51串行通讯底层驱动程序,由头文件serint.hJ及serint.c组成。 返回页首
serint.h 下载serint.h
unsigned char RR_iHead; /*receiver head index */
unsigned char RR_iTail; /*receiver tail index */
unsigned char RR_cLev; /*receiver buffer count */
unsigned char RR_cMax; /*receiver buffer count */
unsigned char TR_iHead; /*transmitter head index */
unsigned char TR_iTail; /*transmitter tail index */
unsigned char TR_cLev; /*transmitter buffer count */
unsigned char TR_cMax; /*transmitter buffer count */
unsigned char UnGotCh; /*saved char for ungetch()*/
unsigned char SerFlags; /*serial flag */
bit FlagTransIdle; /*set when transmitter is finished */
bit FlagStripOutLF; /*don't send linefeeds */
bit FlagCvtInCR; /*convert incoming CRto LF*/
unsigned char TestBits;
#define INRINGSIZE128 /*must be <=254to avoid wraps */
#define OUTRINGSIZE250 /*ditto */
#define T1RELOAD253
#define CR13
#define LF10
#define ESC27
#define EOF-1
unsigned char xdata RRing[INRINGSIZE]; /*receiver ring buffer */
unsigned char xdata TRing[OUTRINGSIZE]; /*receiver ring buffer */
int putstr (const char *);
int putch(int);
int chkch();
int getch();
void SerWaitOutDone();
int SerFlushIn();
int putc(int TransChar);
serint.c 下载seint.c
/*CONSOLE.C--serial I/Ocode */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 返回页首
/*Initialize serial port hardware and variables */
#include <reg51.h>
#include "serint.h"
void SerInitialize(){
SerFlags =0;
FlagTransIdle =1;
FlagCvtInCR=1; /*want to turn CRs into LFs */
RR_iHead =RR_iTail =RR_cLev =RR_cMax =0;
TR_iHead =TR_iTail =TR_cLev =TR_cMax =0;
UnGotCh =-1;
/*---set up Timer 1to produce serial rate */
TCON&=0x3F; /*clear run
&interrupt flags */
TMOD&=0x0F; /*flush existing Timer 1setup */
TMOD|=0x20; /*flush existing Timer 1setup */
SCON=0x50; /*flush existing Timer 1setup */
PCON|=0x00;
TH1=TL1=T1RELOAD&0x00FF; /*flush existing Timer 1setup */
TR1=1; /*start the timer */
ES=1; /*enable serial interrupts */
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 返回页首
/*Serial console interrupt handler */
/*If transmitter output is disabled,we fake trans interrupts until empty */
void SerInt()interrupt 4
{
if(RI){ /*receiver interrupt
active?*/
if(RR_cLev<INRINGSIZE){/*room for newest char?*/
RRing[RR_iHead]=SBUF;/*pick up the character and stick in ring */
RR_iHead++; /*tick the index */
RR_cLev++; /*tick size counter */
if(RR_iHead==INRINGSIZE)RR_iHead =0; /*hit end of array yet?*/
}
RI=0; /*indicate we have it
*/
}
if(TI){ /*transmitter
interrupt active?*/
if(TR_cLev){ /*anything to send?*/
SBUF=TRing[TR_iTail];/*fetch next char and send it */
TR_cLev--; /*tick size counter */
TR_iTail++; /*tick the index */
if(TR_iTail==OUTRINGSIZE)TR_iTail =0; /*hit end of array yet?*/
}else FlagTransIdle =1;/*no,flag inactive */
TI=0; /*indicate done with it
*/
}
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 返回页首
/*Send character to console */
/*Can strip LFs,in which case you get CRinstead of LF/CR*/
int putch(int TransChar)
{
putc(TransChar); /*if not LF,handle
normally */
if(TransChar=='\n')putc('\r'); /*if LF,send a CR*/
}
int putc(int TransChar)
{
while(TR_cLev>=OUTRINGSIZE); /*wait for space in ring */
ES=0;
TRing[TR_iHead]=TransChar; /*point to char slot */
TR_iHead++; /*tick
counter &index */
TR_cLev++;
if(TR_iHead==OUTRINGSIZE)TR_iHead =0;
if(FlagTransIdle){
FlagTransIdle =0; /*kickstart transmitter if idle */
TI=1;
}
ES=1;
return(TransChar);
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/*Decide if there are any pending chars */
/*Returns nonzero if there's a char */
int chkch(){
return(RR_cLev); /*tack on current
level */
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 返回页首
/*Wait for the serial transmitter to go idle */
/*If the transmitter is disabled,that's considered to be the same thing */
void SerWaitOutDone(){
while (TR_cLev); /*wait for ring
empty */
while(!FlagTransIdle); /*wait for last char */
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 返回页首
/*Flush the input buffer */
/*Returns number of chars flushed */
int SerFlushIn(){
ES=0; /*turn
off serial interrupts */
RR_iTail =0; /*reset
ring variables */
RR_iHead =0;
RR_cLev =0;
ES=1; /*turn
on serial interrupts */
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 返回页首
/*Get character from console */
/*CRs turn into LFs unless we're not doing that...*/
int getch(){
int RetVal;
ES=0; /*avoid interruptions */
if(RR_cLev){ /*anything pending?*/
RetVal =RRing[RR_iTail];
if(RetVal=='\r')RetVal ='\n'; /*use LFinstead of CR*/
RR_iTail++; /*tick size index &counter */
RR_cLev--;
if(RR_iTail==INRINGSIZE)RR_iTail =0;/*hit end of array yet?*/
}else RetVal =-1;
ES=1;
return(RetVal);
}
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/ 返回页首
/*Send string to console */
/*putstr(char *pString);*/
/*The ?putstr entry point has *pString in DPTR*/
int putstr (char *pstring)
{
while(*pstring){ /*fetch character if zero done */
putch(*pstring);
pstring++; /*continue...*/
}
}
使用查询的程序可以做到多高的波特率取决于主程序的工作量,使用中断方式的通讯驱动程序在使用11.0592MHz晶振时可以达到57.6Kbps的速率。
(5)关于RS485 返回页首
以上几个方面详细介绍了PC及MCS-51的RS-232C的串行通讯程序的设计方法,RS-485与RS-232C相类似,其区别在于使用双端平衡驱动及半双工模式,这些措施使RS-485传输距离更远,同时,RS-485还可以组网。在同一个RS-485网络中,可以多达32个模块,某些器件可以多达256个甚至更多。相应的,RS-485具有接收/发送控制端,RS-485的接收控制端可以在需要接收的时候打开或者一直打开以便无条件的接收线路上的数据。RS-485的发送控制端仅在需要发送时打开,平时应关端发送器,因为在同一RS-485网络中在同一时刻仅允许一个发送器工作。在数据发送完成后关闭发送器。这可以通过以下两种方法实现。
一、在数据完全移出后,对于PC机为发送移位寄存器空,对于MCS-51为TI置位。这些调件既可使用查询的方法得到,也可以在中断程序中实现。
二、将RS-485的接收器始终打开,这样一来,所有在RS-485上的数据均被接收回来,包括自己发送出去的数据。因此,当自己发送的数据完全被自己接收回来时即可关闭发送器。原则上说,这一方法无论是查询或中断方式都适用,但实际上,由于RS-485的数据通常打包后发送,因此,使用查询的方法并不理想。这一方法非常适合中断方式,尤其是以数据包传送的RS-485通讯。
|